تواصل مع فريقنا

- 3117
Introduction
Imagine, converting the residual material of sugar processing into sustainable tableware, packaging materials and even energy sources. As sugarcane is considered one of the most grown crops in the world, it makes huge portions of waste products. Of all these byproducts, bagasse is unique and versatile as well as enormous. Sugarcane bagasse is an example of a once discarded product that is currently leading the fight in developing eco-friendly, disposable products as alternatives to plastic and paper.
The topic of using sugarcane bagasse can be important to both businesses and consumers, trying as they might be to make at least some choices which involve less environmental impact or which otherwise relate to the ideals of a circular economy.
In this blog, we will discover how sugarcane byproducts may become a source of renewable innovations- and how bagasse tableware and packaging are becoming a more sustainable future.
What is Sugarcane Waste and Bagasse?
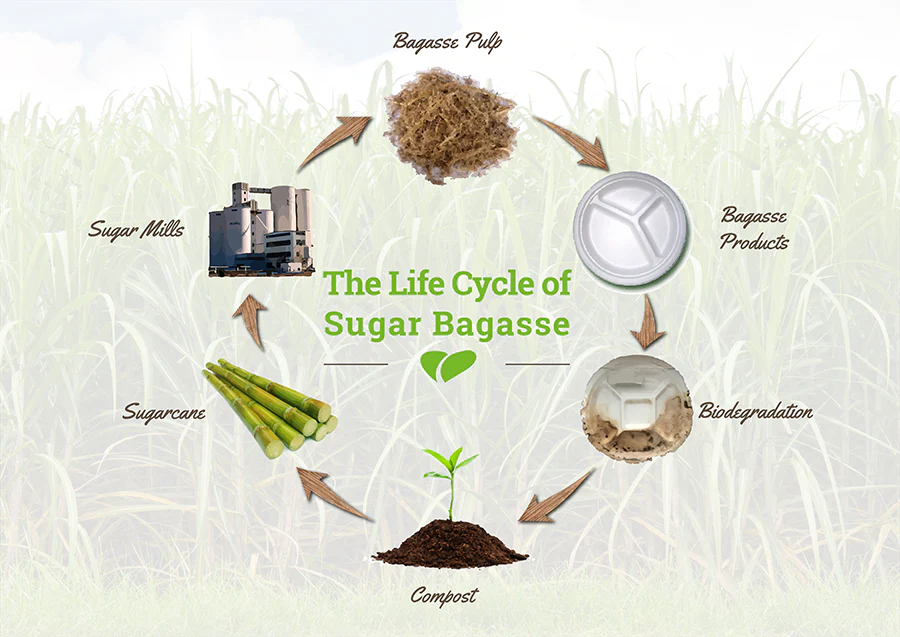
Sugarcane waste is the byproduct of the production of juice obtained by crushing sugarcane stalks. This entails molasses, filter mud, and the most prevalent component which is bagasse.
Bagasse refers to the fibrous dry material that remains, when sugarcane stalks are crushed. Millions of tons of this byproduct are produced worldwide each year. As an example, India alone generates more than 100 million tons of sugarcane waste annually, and much of this amount consists of bagasse.
But why is this important? Reuse of waste sugarcane bagasse is not just an environmental requirement, but also a resource that industries want to utilize in the bid to minimize their use of plastic and wood-related products.
Why Focus on Bagasse?
Renewable & Abundant: It is a byproduct of an already large-scale agricultural sector.
Biodegradable: Bagasse breaks down naturally in 60 to 90 days as opposed to plastic which takes hundreds of years to degrade.
Low Carbon Impact: The use of bagasse prevents disposal in incinerators or landfills, which result in greenhouse gas emissions.
The use of sugarcane bagasse is a scalable method of making businesses reduce their carbon footprint and achieve their sustainability target. It is an excellent alternative to paper (deforestation problem) and plastic (pollution problem), and it is a backbone of being eco-friendly innovation.
How Is Bagasse Used?
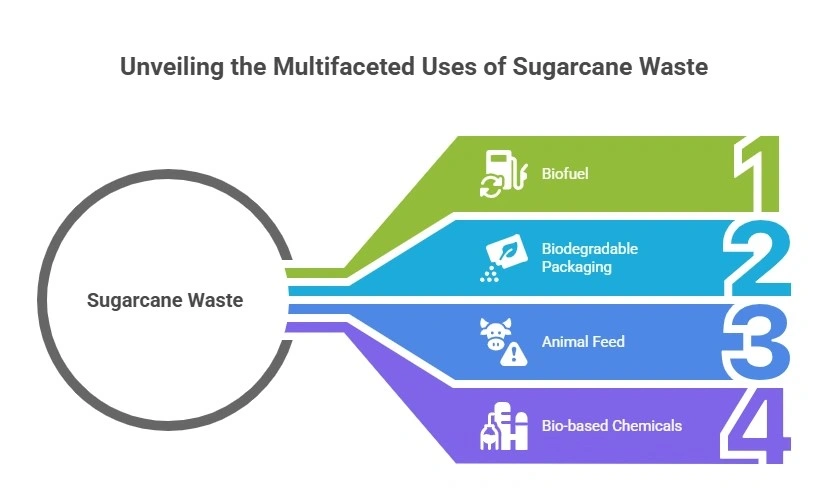
Bagasse Tableware
One of the most popular sugarcane waste products is bagasse tableware, a biodegradable alternative to single-use plastic plates, bowls, cups, and cutlery.
These products are:
• Durable and sturdy
• Heat- and cold-resistant
• Microwave-safe
• Compostable, breaking down in commercial compost facilities
Consumers and food service providers are increasingly opting for bagasse tableware because it provides all the functionality of plastic, without the environmental cost.
Bagasse Packaging Solutions
In addition to tableware, bagasse packaging has gained momentum in industries such as takeout food services, grocery stores, and e-commerce.
Applications include:
• Food containers and trays
• Beverage holders
• Protective packaging for electronics or fragile items
As legislation tightens around plastic use, bagasse packaging is helping companies stay compliant while reducing their environmental impact.
Energy Production
Beyond physical products, bagasse used for energy generation is a growing trend.
Sugar mills burn bagasse to produce:
• Electricity
• Steam for internal operations
This bioenergy is clean and renewable, often contributing surplus electricity to national power grids. In essence, sugarcane bagasse waste is fueling a low-carbon future.
The Environmental Benefits of Bagasse
Reducing Plastic Waste
Plastic items are wasted in landfills and oceans every year, the number of those items being in billions. Bagasse tableware and packaging can be used to offset this burden as it provides a compostable option.
Minimizing Carbon Footprint
There is also a reduction in the emission of greenhouse gases through re-purposing sugarcane remnants as opposed to allowing them to decompose and produce methane gas. Also, products made of bagasse will have a much lower lifecycle carbon footprint than those made of plastic or paper.
Advancing the Circular Economy
Bagasse is an example of the circular economy, and this means that they make use of agricultural waste to create valuable and useful products. It has an end-to-end cycle on production, use, and natural breakdown.
Terms like “sugarcane bagasse waste” and “use of sugarcane bagasse” aren't just buzzwords—they're central to building a sustainable world.
Exploring Challenges in Bagasse Waste Management
Transportation and Storage
Bagasse is bulky and retains moisture, making it difficult to store and transport efficiently without proper drying and compacting methods.
Infrastructure Barriers
Not all regions have the necessary facilities to convert bagasse into usable products. Investment in processing plants is crucial to broaden adoption.
Environmental Risks
Improperly stored bagasse can attract pests or cause mold issues. If burned without pollution controls, it may contribute to air pollution. Advanced waste-to-resource technologies are helping mitigate these risks.
Innovations Driving the Future of Bagasse Products
Advanced Bio-Plastics
Researchers are developing bagasse-derived bioplastics that mimic the strength and flexibility of petroleum-based plastics—without the pollution.
Tech-Driven Solutions
AI, robotics, and smart drying systems are being used to enhance bagasse processing. Companies are also experimenting with 3D printing and nanotech to create high-performance materials from sugarcane waste.
Market Growth
With governments banning plastic and businesses seeking eco-labels, demand for bagasse packaging and tableware is surging. The global biodegradable packaging market is projected to surpass $100 billion by 2030—and bagasse is leading the charge.
Conclusion
What was once a forgotten waste product of sugarcane is now a star player in the fight against environmental degradation. Bagasse has proven to be more than just residue—it’s a renewable, compostable, and innovative material powering the sustainable solutions of tomorrow. From tableware and packaging to energy generation, the use of sugarcane bagasse is rewriting the narrative on waste and sustainability.
Ready to make a difference? Start by choosing bagasse products for home, office, or business. Every purchase supports a cleaner planet and a circular economy.
© 2024 , Goldleaf ,
جميع الحقوق محفوظة.
Made & Managed by Lightlink Solutions




